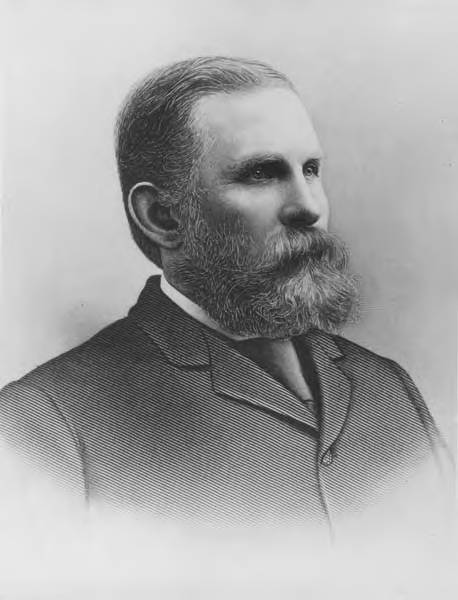
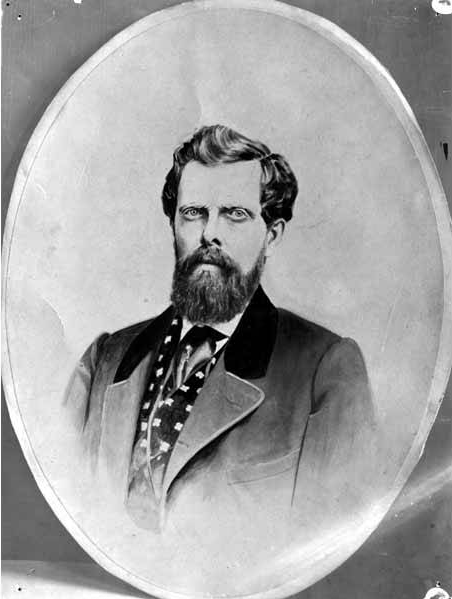
This street is named after Charles Carroll Terry (1830–1867), one of the members, along with his older brother, Lee, of the Denny Party that landed at Alki Point in November 1851. Shortly after the landing, he opened the first store in King County. Lee had made a land claim in Alki a few months earlier, but went home to New York the next year; Charles remained, even after most of the other settlers left for what is now Pioneer Square. It seems he finally moved north in 1857, trading his Alki land for that of David Swinson “Doc” Maynard in Pioneer Square. He died 10 years later, according to this biography, of tuberculosis. (Whether or not he and his brother were responsible for naming the Alki Point settlement New York, which became New York–Alki [the latter word meaning ‘by and by’ or ‘someday’ in Chinook Jargon] and then just Alki, is unclear, although he did officially apply the Alki name to the town plat he filed in 1853.)
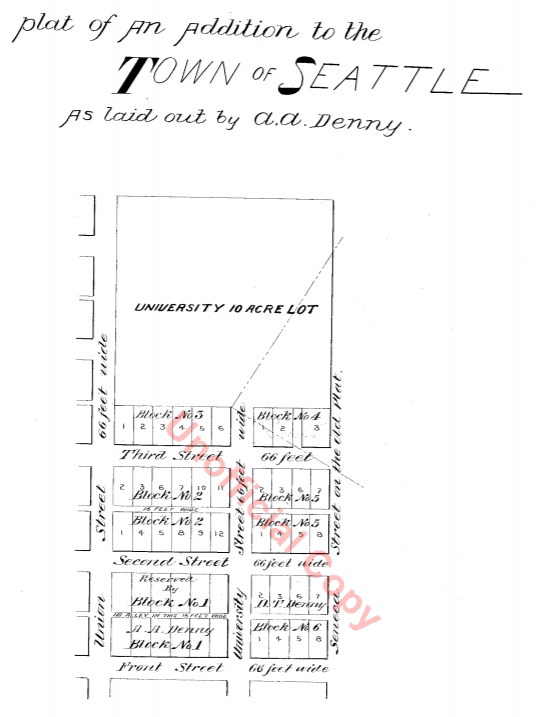
In 1855, he, along with Edward Lander, bought Carson Boren’s downtown land claim for $500; he and Lander donated two acres to form the first campus of the University of Washington, which opened in 1861. (He named one of his sons, born in 1862, Edward Lander Terry.) His name also appears on Terry Hall, a UW dormitory on NE Campus Parkway.

Terry Avenue begins at Alder Street on First Hill and goes ½ a mile to Spring Street, where it is blocked by Virginia Mason Hospital. Resuming at Seneca Street, it goes ⅕ of a mile to Pike Street. On the other side of Interstate 5 and the Washington State Convention Center, it begins again at Howell Street and goes ⅘ of a mile to Valley Street and Lake Union Park, becoming Terry Avenue N as it crosses Denny Way. Amazon.com’s headquarters are at 410 Terry Avenue N, between Harrison Street and Republican Street.
Born and raised in Seattle, Benjamin Donguk Lukoff had his interest in local history kindled at the age of six, when his father bought him settler granddaughter Sophie Frye Bass’s Pig-Tail Days in Old Seattle at the gift shop of the Museum of History and Industry. He studied English, Russian, and linguistics at the University of Washington, and went on to earn his master’s in English linguistics from University College London. His book of rephotography, Seattle Then and Now, was published in 2010. An updated version came out in 2015.